What are Cannabinoids?
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and CBD (cannabidiol) are two of the more than 100 naturally occurring chemical compounds referred to as cannabinoids. The human endocannabinoid system (ECS) and the cannabis plant, along with many other botanicals, both produce these substances. In the bodies of humans and many other animals, they interact with cannabinoid receptors in the endocannabinoid system to produce a range of non-psychoactive and psychoactive effects.
Cannabinoids are categorized as phytocannabinoids or endocannabinoids depending on their source. The prefix “phyto” means “plant,” and refers to phytocannabinoids’ plant-based origin. The word “endo” in endocannabinoids means “within,” implying that these cannabinoids are produced within the body. Both phytocannabinoids and endocannabinoids interact with the nervous system’s endocannabinoid system.
Each cannabinoid may have a different effect on the body when consumed alone, but when combined, cannabinoids may increase the overall functional advantages of the cannabis plant.
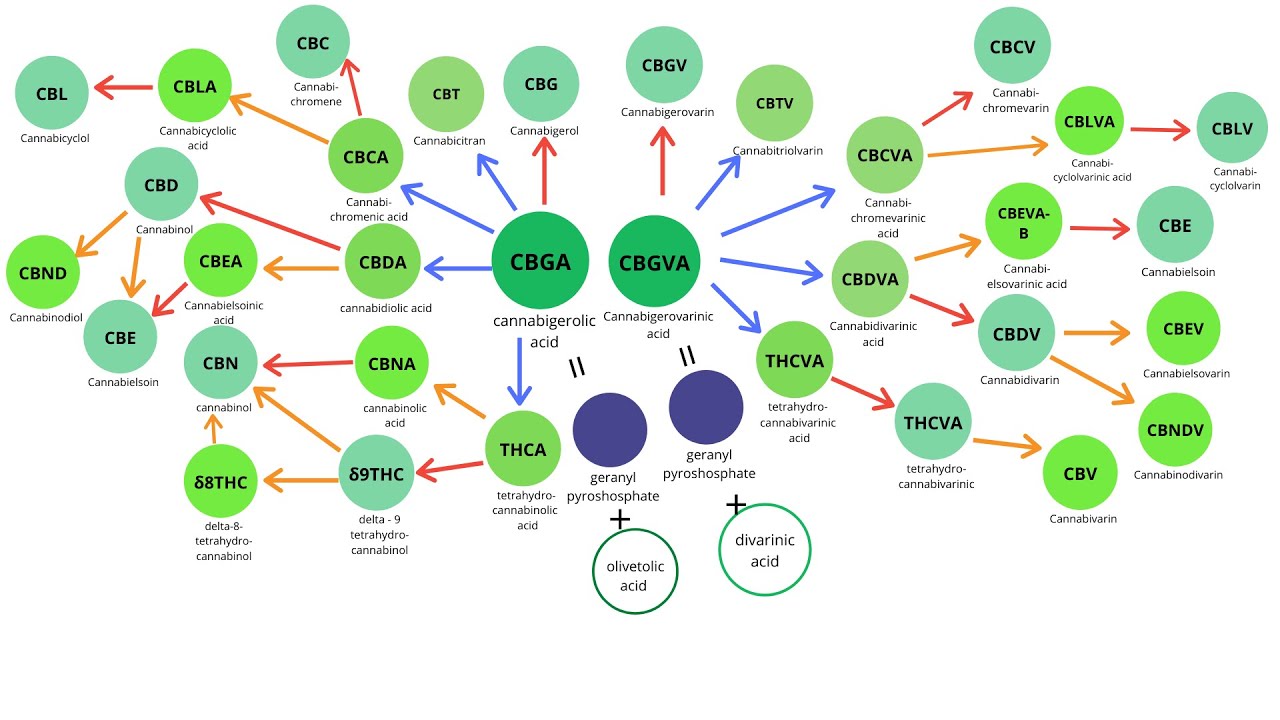
Minor cannabinoids include cannabinol (CBN), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabidioloic acid (CBDA), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), cannabinolic acid (CBNA), cannabidivarin (CBDV), tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), cannabigerovarin (CBGV), cannabichromevarin (CBCV), and others (Hanus, et al., 2016; Gülck and Möller, 2020).
Cannabinoids appear naturally in the cannabis plant in their acidic forms and are thought to confer antioxidant and defense mechanisms (insecticidal, antimicrobial, etc.,) to the plant. Acidic cannabinoids undergo decarboxylation during heating and are converted to the corresponding neutral cannabinoids . For example, THCA is converted to Δ9-THC when cannabis is smoked or vaporized. Some decarboxylation also occurs with passage of time at room temperature and during exposure to light.
Cannabis products intended to contain the acidic forms of cannabinoids nearly universally also contain low levels of cannabinoids in their neutral forms. The varinic cannabinoids are considered rare but are now emerging as new targets of selective breeding. Varin compounds such as CBDV and THCV contain two fewer carbon atoms than their non-varin counterparts (CBD and Δ9-THC) endowing these cannabinoids with unique pharmacological properties .
The overall pharmacological action of the minor cannabinoids often results from binding at both cannabinoid and “off target” receptors. This combination of receptor-mediated actions makes them well suited as multi-target therapeutic agents.